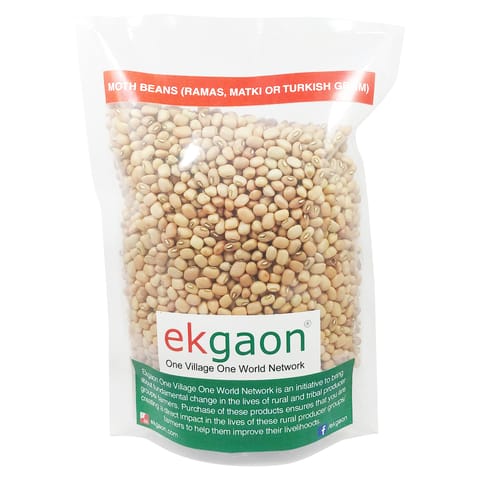
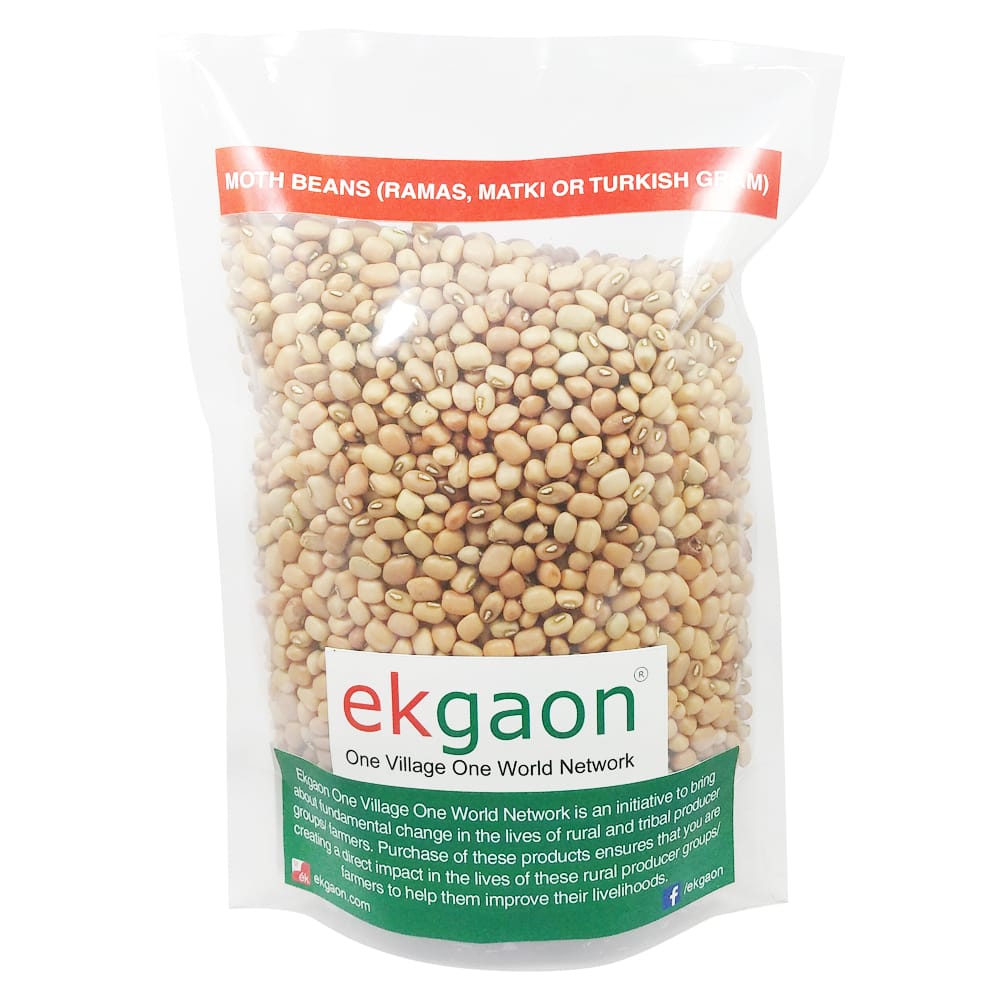
Vigna aconitifolia or popuarly called Moth Bean is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called ramas, mat bean, moth bean, matki, Turkish gram or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume. Due to its drought resistant qualities, its ability to combat soil erosion and its high protein content, moth bean has been identified as a major source of rich food of the future. Whole or split moth bean seeds can be cooked or fried. In India, particularly in the state of Maharashtra, moth beans are sprouted before cooking and used for making Usal (spicy stew). They can be used for breakfast or other meals, and is popular as such in north India. The moth bean pods can be boiled and eaten, and seeds can be ground into flour that is used for another traditional namkeen called bhujia. Moth beans are rich in nutrition, 100g of raw, uncooked moth bean seeds contain 343 calories, 23 g of protein, 62 g of carbohydrate and 1.6 g of fat.As is the case with other legumes, this pulse does contain antinutritional factors that limit available protein. Soaking and cooking moth beans before consumption helps to break down antinutritional factors and makes the protein more digestible.
EG134- Home
- Top Values
- Gluten Free
- Moth Beans (Ramas, Matki or Turkish Gram) (1.5kg)
Moth Beans (Ramas, Matki or Turkish Gram) (1.5kg)
- The moth bean pods can be boiled and eaten, and seeds can be ground into flour that is used for another traditional namkeen called bhujia.
- Moth beans are rich in nutrition, 100g of raw, uncooked moth bean seeds contain 343 calories, 23 g of protein, 62 g of carbohydrate and 1.6 g of fat
- As is the case with other legumes, this pulse does contain antinutritional factors that limit available protein.
- Soaking and cooking moth beans before consumption helps to break down antinutritional factors and makes the protein more digestible.
The product is at its best price.
- Easy Returns
- 100% Authentic Products
- Secure Payments
Vigna aconitifolia or popuarly called Moth Bean is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called ramas, mat bean, moth bean, matki, Turkish gram or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume. Due to its drought resistant qualities, its ability to combat soil erosion and its high protein content, moth bean has been identified as a major source of rich food of the future. Whole or split moth bean seeds can be cooked or fried. In India, particularly in the state of Maharashtra, moth beans are sprouted before cooking and used for making Usal (spicy stew). They can be used for breakfast or other meals, and is popular as such in north India. The moth bean pods can be boiled and eaten, and seeds can be ground into flour that is used for another traditional namkeen called bhujia. Moth beans are rich in nutrition, 100g of raw, uncooked moth bean seeds contain 343 calories, 23 g of protein, 62 g of carbohydrate and 1.6 g of fat.As is the case with other legumes, this pulse does contain antinutritional factors that limit available protein. Soaking and cooking moth beans before consumption helps to break down antinutritional factors and makes the protein more digestible.
Vigna aconitifolia or popuarly called Moth Bean is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called ramas, mat bean, moth bean, matki, Turkish gram or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume. Due to its drought resistant qualities, its ability to combat soil erosion and its high protein content, moth bean has been identified as a major source of rich food of the future. Whole or split moth bean seeds can be cooked or fried. In India, particularly in the state of Maharashtra, moth beans are sprouted before cooking and used for making Usal (spicy stew). They can be used for breakfast or other meals, and is popular as such in north India. The moth bean pods can be boiled and eaten, and seeds can be ground into flour that is used for another traditional namkeen called bhujia. Moth beans are rich in nutrition, 100g of raw, uncooked moth bean seeds contain 343 calories, 23 g of protein, 62 g of carbohydrate and 1.6 g of fat.As is the case with other legumes, this pulse does contain antinutritional factors that limit available protein. Soaking and cooking moth beans before consumption helps to break down antinutritional factors and makes the protein more digestible.
Vigna aconitifolia or popuarly called Moth Bean is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called ramas, mat bean, moth bean, matki, Turkish gram or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume. Due to its drought resistant qualities, its ability to combat soil erosion and its high protein content, moth bean has been identified as a major source of rich food of the future. Whole or split moth bean seeds can be cooked or fried. In India, particularly in the state of Maharashtra, moth beans are sprouted before cooking and used for making Usal (spicy stew). They can be used for breakfast or other meals, and is popular as such in north India. The moth bean pods can be boiled and eaten, and seeds can be ground into flour that is used for another traditional namkeen called bhujia. Moth beans are rich in nutrition, 100g of raw, uncooked moth bean seeds contain 343 calories, 23 g of protein, 62 g of carbohydrate and 1.6 g of fat.As is the case with other legumes, this pulse does contain antinutritional factors that limit available protein. Soaking and cooking moth beans before consumption helps to break down antinutritional factors and makes the protein more digestible.
| VARIANT | SELLER | PRICE | QUANTITY |
|---|
Product Enquiry Form
Leave us a message for futher information.
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Thanks, You have now been subscribed to our newsletter.
Your response has been recorded.
Get news and offers delivered straight to your inbox. We promise to never spam.
- Facing Issues? Call us Mon-Fri between 11 AM - 7 PM
- +919830476761
www.onahealthynote.com